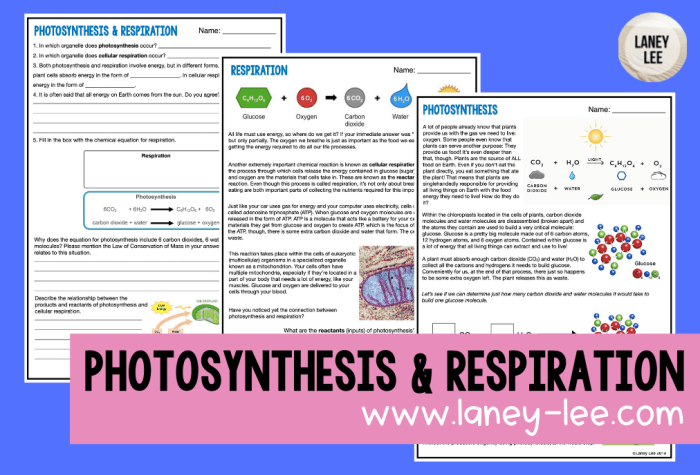
Embark on a scientific expedition with the photosynthesis HHMI BioInteractive answer key, your indispensable guide to unraveling the intricate mechanisms of plant life. This comprehensive resource empowers you to delve into the fundamental processes of photosynthesis, shedding light on its historical significance and ecological implications.
Through a captivating exploration of light-dependent reactions, the structure and function of chloroplasts, and the intricacies of the Calvin cycle, you will gain a profound understanding of how plants harness light energy to transform carbon dioxide and water into life-sustaining carbohydrates.
Overview of Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis Hhmi Biointeractive Answer Key
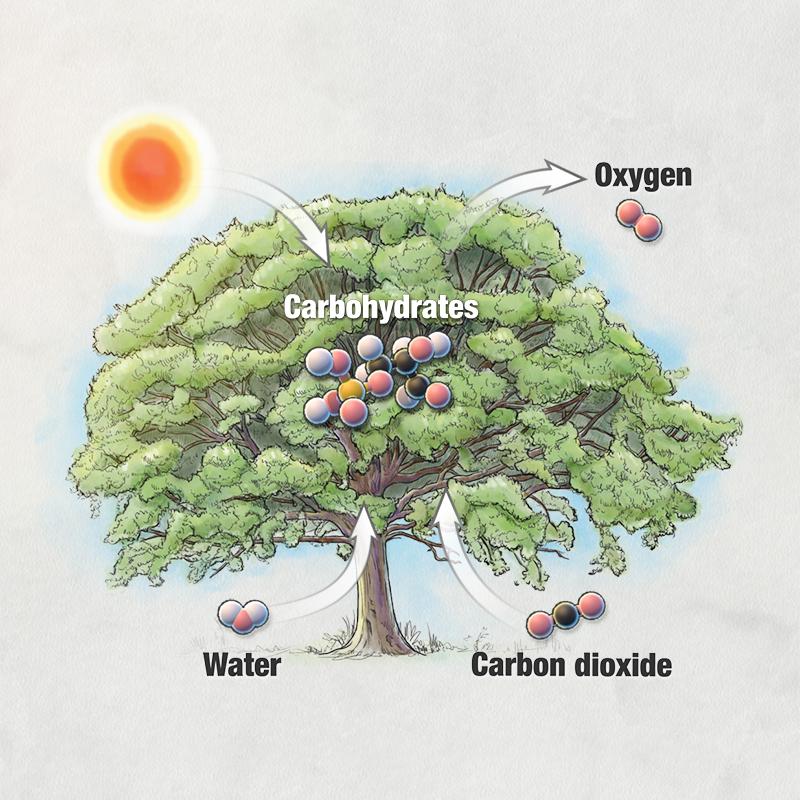
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process that converts light energy into chemical energy, resulting in the production of organic compounds from inorganic substances. It is essential for life on Earth, as it provides the primary source of food and oxygen for most living organisms.
The history of photosynthesis research dates back to the 17th century with the discovery of oxygen release by plants in sunlight by Jan Ingenhousz. Further advancements in the understanding of photosynthesis were made by Joseph Priestley and Jan Ingenhousz, who demonstrated the role of light and plants in producing oxygen.
The concept of photosynthesis as a chemical process was proposed by Julius von Sachs in the 19th century.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Light-dependent reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis and occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. These reactions utilize light energy to produce ATP and NADPH, which are energy-carrier molecules.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, a green pigment responsible for absorbing light energy. The structure of chloroplasts includes thylakoid membranes stacked into grana, which provide a large surface area for light absorption.
Light absorption by chlorophyll initiates a series of energy transfer reactions involving other pigments and electron carriers. This energy transfer results in the production of ATP and NADPH, which are then used in the Calvin cycle.
Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions)
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. It utilizes the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose.
The Calvin cycle consists of three main steps: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. Carbon fixation involves the incorporation of carbon dioxide into organic molecules, primarily ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
Reduction involves the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P), utilizing the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions. G3P is a sugar molecule that can be used to synthesize glucose or other carbohydrates.
Regeneration involves the recycling of RuBP to continue the cycle. This step utilizes ATP and releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
Environmental Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is influenced by various environmental factors, including light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration.
Light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis up to a certain point. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until it reaches a plateau. This is because light energy is required for the light-dependent reactions.
Temperature also affects the rate of photosynthesis, with an optimal temperature range for most plants. Temperatures outside this range can inhibit the activity of enzymes involved in photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide concentration affects the rate of photosynthesis, as it is a substrate for the Calvin cycle. Increasing carbon dioxide concentration can increase the rate of photosynthesis until a saturation point is reached.
Importance of Photosynthesis, Photosynthesis hhmi biointeractive answer key
Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth, as it provides the primary source of food and oxygen for most living organisms.
Photosynthesis plays a vital role in the global carbon cycle, as it removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into organic compounds. This process helps regulate the Earth’s climate.
Photosynthesis has significant economic and agricultural importance. It provides the basis for food production and supports various industries, including agriculture, forestry, and biofuel production.
User Queries
What is the significance of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth as it produces oxygen and carbohydrates, which are essential for respiration and energy production, respectively.
How does light intensity affect photosynthesis?
Light intensity directly influences the rate of photosynthesis, with higher light intensity leading to increased rates of carbon dioxide fixation.
What is the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy, which is used to drive the reactions of photosynthesis.