What is the approximate diameter of the mature parent cell – The approximate diameter of a mature parent cell is a critical aspect of cell biology, influencing cell function and division. Understanding this measurement provides insights into the fundamental processes that govern cellular life.
Parent cells, the precursors to daughter cells, undergo maturation influenced by various factors. The diameter of these cells varies across cell types, necessitating precise measurement techniques.
1. Definition of Parent Cell
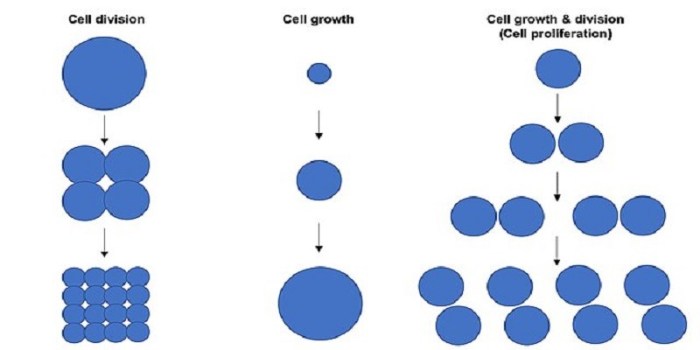
In cell biology, a parent cell refers to the cell that undergoes division to produce two or more daughter cells. Parent cells contain the complete set of genetic material and organelles necessary for the formation of new cells.
Parent cells play a crucial role in cell division, which is essential for growth, development, and repair in living organisms. During cell division, the parent cell undergoes a series of complex processes to ensure the accurate segregation of genetic material and organelles into the daughter cells.
2. Maturation of Parent Cells: What Is The Approximate Diameter Of The Mature Parent Cell
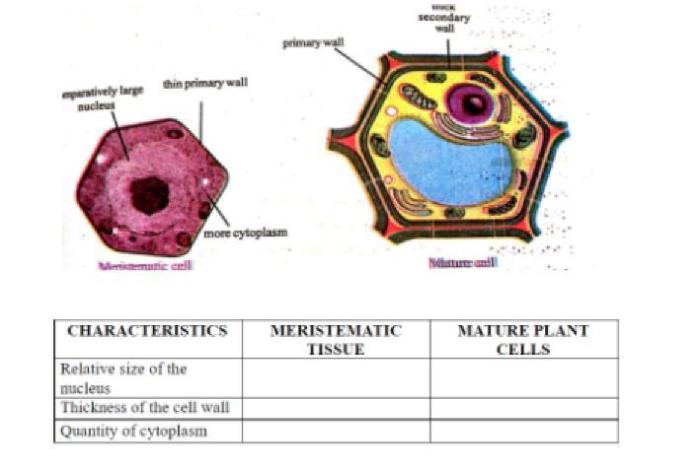
The maturation of parent cells involves a series of preparatory steps before cell division can occur. This process includes:
- DNA replication:The parent cell duplicates its entire genome to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information.
- Organelle duplication:Essential organelles, such as mitochondria and ribosomes, are duplicated to ensure that each daughter cell has the necessary cellular machinery.
- Growth and enlargement:The parent cell undergoes growth and enlargement to accommodate the duplicated genetic material and organelles.
3. Size of Mature Parent Cells
The diameter of mature parent cells varies depending on the cell type and organism. However, general ranges can be provided:
- Eukaryotic cells:Typically range from 10 to 100 micrometers (µm) in diameter.
- Prokaryotic cells:Typically range from 0.5 to 5 µm in diameter.
Within each cell type, there can be significant variability in diameter. For example, mature red blood cells in humans have a diameter of approximately 7 µm, while mature muscle cells can be several hundred micrometers in diameter.
4. Methods for Measuring Parent Cell Diameter
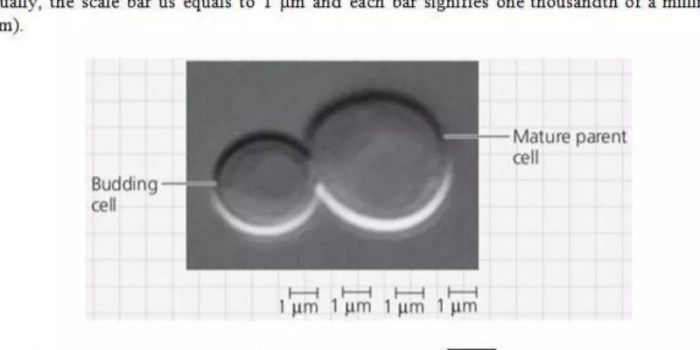
Various methods are used to measure the diameter of parent cells, including:
- Microscopy:Using a microscope with a calibrated scale to measure the cell’s diameter directly.
- Flow cytometry:A technique that uses a laser to measure the size and shape of cells as they flow through a narrow channel.
- Coulter counter:A device that measures the electrical impedance of cells as they pass through a small aperture, which can be used to determine cell size.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, such as accuracy, precision, and throughput.
5. Significance of Parent Cell Diameter
The diameter of parent cells has important implications for cell biology:
- Cell function:The size of a parent cell can influence its function. For example, larger parent cells may have a greater capacity for protein synthesis or storage.
- Cell division:The diameter of the parent cell can affect the mode of cell division. For instance, larger parent cells may undergo mitosis, while smaller parent cells may undergo binary fission.
- Cell differentiation:The size of parent cells can also influence cell differentiation, as different cell types have characteristic sizes.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of parent cell diameter?
Parent cell diameter is important because it affects the size and function of daughter cells. It also influences the rate of cell division and the overall growth and development of the organism.
How is parent cell diameter measured?
Parent cell diameter can be measured using various techniques, including microscopy, flow cytometry, and image analysis. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific cell type and the desired level of accuracy.
What factors influence parent cell diameter?
Parent cell diameter is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental conditions, and cell cycle stage. The availability of nutrients, growth factors, and hormones can also affect parent cell diameter.
