Art labeling activity antibody structure – In the realm of art and science, the “Art Labeling Activity: Antibody Structure” emerges as a captivating fusion, offering an innovative approach to understanding the intricacies of antibody structure. This activity transforms the complex world of antibodies into an artistic canvas, fostering a deeper comprehension through hands-on engagement.
Art labeling activities empower students to visualize and interpret the distinct domains and functions of antibodies, translating abstract concepts into tangible representations. By engaging with art as a medium of learning, students embark on a journey that enriches their understanding of antibody structure and its significance in the immune system.
Antibody Structure
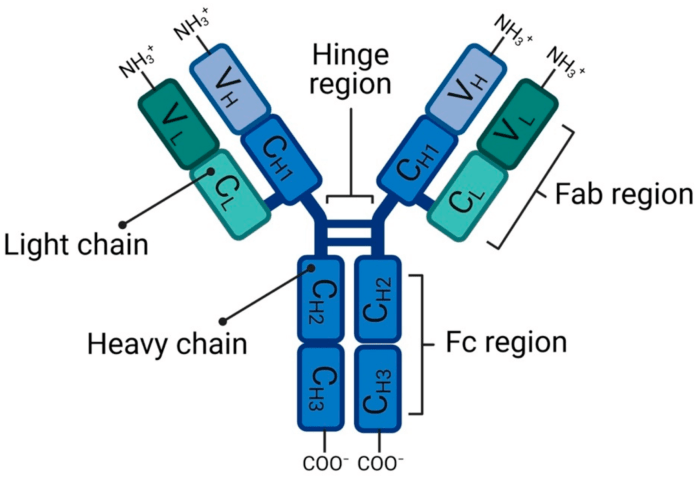
Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that are produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
The basic structure of an antibody consists of four polypeptide chains: two heavy chains and two light chains. The heavy and light chains are held together by disulfide bonds to form a single molecule.
Each antibody molecule has two antigen-binding sites, which are located at the tips of the Y-shaped molecule. The antigen-binding sites are highly specific for a particular antigen, and they allow the antibody to bind to and neutralize the antigen.
Domains of an Antibody
The antibody molecule is divided into several domains, each with a specific function.
- Variable domains:The variable domains are located at the tips of the Y-shaped molecule and contain the antigen-binding sites. The variable domains are highly variable in sequence, which allows the antibody to bind to a wide range of antigens.
- Constant domains:The constant domains are located at the base of the Y-shaped molecule and are responsible for the effector functions of the antibody. The constant domains are less variable in sequence than the variable domains.
- Hinge region:The hinge region is a flexible region that connects the variable domains to the constant domains. The hinge region allows the antibody to change its shape to bind to different antigens.
Role of Disulfide Bonds, Art labeling activity antibody structure
Disulfide bonds play an important role in maintaining the structure of an antibody.
The disulfide bonds between the heavy and light chains hold the antibody molecule together and prevent it from falling apart.
The disulfide bonds between the variable and constant domains help to maintain the shape of the antigen-binding site.
Popular Questions: Art Labeling Activity Antibody Structure
What are the benefits of using art labeling activities in the classroom?
Art labeling activities enhance visual learning, promote creativity, and foster a deeper understanding of complex scientific concepts.
How can art labeling activities help students visualize the three-dimensional structure of an antibody?
By creating physical or digital representations of antibodies, students can visualize the spatial arrangement of different domains and their interactions.