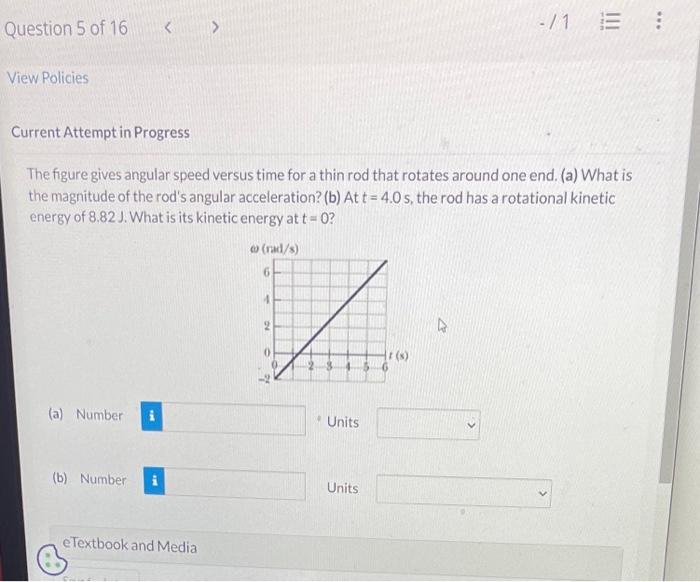
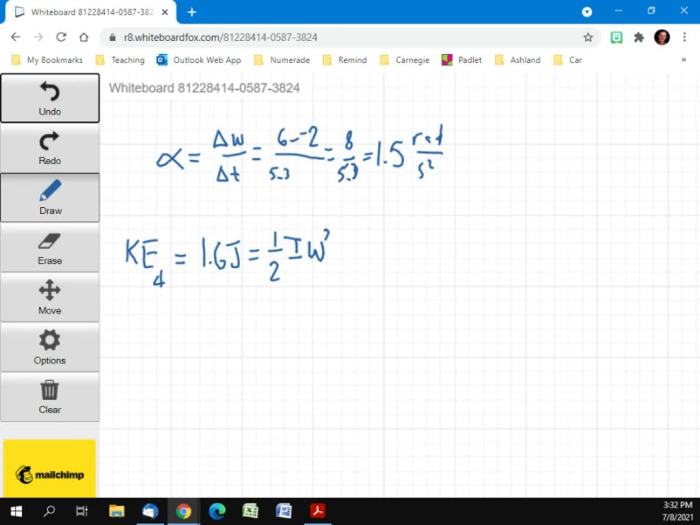
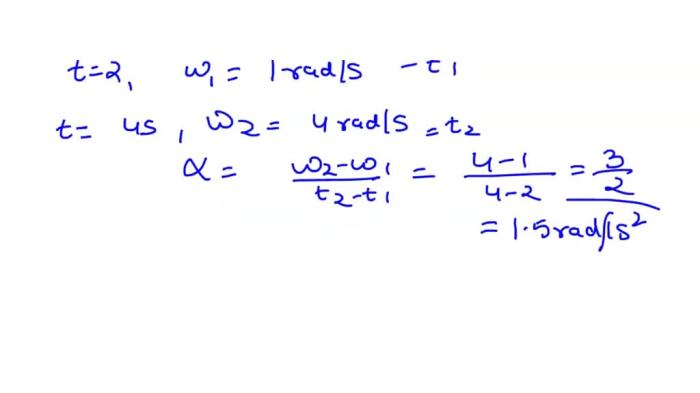The figure gives angular speed versus time, a graph that illustrates the relationship between an object’s angular speed and the time elapsed. Angular speed, measured in radians per second, quantifies the rate at which an object rotates around an axis.
This graph provides valuable insights into the object’s rotational motion.
The graph’s slope signifies the object’s angular acceleration, indicating whether its angular speed is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Different graph patterns represent distinct types of motion, such as uniform circular motion, accelerated rotation, or oscillatory motion.
Definition of Angular Speed: The Figure Gives Angular Speed Versus Time
Angular speed is a measure of how fast an object is rotating. It is defined as the rate of change of the angle of rotation with respect to time. The angular speed of an object is typically measured in radians per second (rad/s).
The mathematical formula for calculating angular speed is:
ω = dθ/dt
where:
- ω is the angular speed in radians per second
- θ is the angle of rotation in radians
- t is the time in seconds
Relationship between Angular Speed and Time
The relationship between angular speed and time can be represented graphically. A graph of angular speed versus time shows the rate of change of angular speed over time. The slope of the graph represents the angular acceleration of the object.
A positive slope indicates that the object is accelerating, while a negative slope indicates that the object is decelerating.
There are different types of graphs that can represent angular speed versus time. A linear graph indicates that the object is rotating at a constant angular speed. A parabolic graph indicates that the object is accelerating or decelerating. A sinusoidal graph indicates that the object is rotating with a periodic motion.
Applications of Angular Speed Analysis
Angular speed analysis is used in a variety of real-world applications. Some examples include:
- Determining the speed of rotating machinery
- Measuring the angular velocity of a projectile
- Analyzing the motion of celestial bodies
- Controlling the speed of motors and engines
Angular speed data can be used to solve problems such as:
- Calculating the distance traveled by a rotating object
- Determining the time it takes for an object to complete a rotation
- Predicting the motion of a rotating object
Angular speed analysis has limitations. For example, it cannot be used to determine the direction of rotation or the axis of rotation.
Methods for Measuring Angular Speed
There are different methods for measuring angular speed. Some common methods include:
- Using a tachometer
- Using a stroboscope
- Using an accelerometer
- Using a laser Doppler vibrometer
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Tachometers are simple to use and relatively inexpensive. Stroboscopes are accurate and can be used to measure the speed of rotating objects that are not visible. Accelerometers are small and can be used to measure the speed of rotating objects that are moving.
Laser Doppler vibrometers are accurate and can be used to measure the speed of rotating objects that are very small.
Factors Affecting Angular Speed, The figure gives angular speed versus time
There are a number of factors that can affect angular speed. Some of these factors include:
- The mass of the object
- The radius of rotation
- The torque applied to the object
- The friction between the object and its surroundings
The mass of the object affects its angular speed because it determines the amount of inertia the object has. The radius of rotation affects the angular speed because it determines the distance that the object must travel to complete a rotation.
The torque applied to the object affects the angular speed because it determines the amount of force that is applied to the object. The friction between the object and its surroundings affects the angular speed because it determines the amount of resistance that the object experiences.
Common Queries
What is angular speed?
Angular speed is the rate at which an object rotates around an axis, measured in radians per second.
How is angular speed calculated?
Angular speed is calculated by dividing the angle of rotation by the time taken to complete the rotation.
What is the relationship between angular speed and time?
The relationship between angular speed and time can be represented graphically, with the slope of the graph indicating the angular acceleration.